Neuromuscular Scoliosis
The Shriners Children's care team has seen tens of thousands of children with neuromuscular scoliosis, the second most common type of scoliosis.
We believe each child deserves an individualized treatment plan utilizing the most advanced and innovative techniques.
Neuromuscular scoliosis is one of three main types of scoliosis, an irregular curve in the spine in the shape of an S or C side to side. It is associated with neuromuscular disorders like cerebral palsy, spina bifida, muscular dystrophy and spinal cord injury.
Because these types of conditions cause muscles to become weak, spastic, or paralyzed, the spine can become destabilized.
In instances where the curve of the spine is more severe and is left untreated, it has the potential to impact the heart, lungs and other internal organs as the child grows.
We have extensive experience in management strategies for patients of all ages and for neuromuscular scoliosis ranging from casting for infantile scoliosis to definitive fusion in adolescents. We also provide growth-friendly solutions for children who require corrective surgery, but who are too young for spinal fusion procedures.
Specific treatments and services may vary by location. Please contact a specific location for more information.
Conditions Associated with Neuromuscular Scoliosis
If your child has one of the below conditions, your child’s team of physicians, surgeons and physical therapists, will likely talk about the possibility of your child developing neuromuscular scoliosis:
Cerebral palsy: The most common birth defect
Spina bifida: A birth defect of the spine where the spinal cord and its coverings (meninges) are exposed through a gap in the backbone
Spinal cord injury: Damage to the spinal cord that results in a loss of function or feeling
Tethered spinal cord: When the spinal cord is stuck to the spinal canal, making development difficult
Muscular dystrophy: A group of inherited diseases that damage and weaken the muscles over time
Symptoms of Neuromuscular Scoliosis
Your child’s pediatrician or their school nurse may have been the first to notice the curve in your child’s spine. As your child continues to grow, you can look for other symptoms to share with their pediatrician and orthopedic specialist. Pay special attention during their teen years when growth spurts are common. Look for symptoms like:
- Leaning to one side
- One shoulder appearing higher than the other
- One shoulder blade sticking out farther than the other
- One hip appearing higher than the other
- Head appearing not properly centered over the body
- When bending from the waist, the ribs on one side are higher
- Waistline appearing flat on one side
- Clothes not fitting correctly
- Hems that aren’t hanging evenly
Talk to us about anything you’ve noticed or have questions about. Once your child is a Shriners Children's patient, we’ll keep a close eye on them with X-rays and other imaging as needed.
Learn About Neuromuscular Scoliosis Treatments
When you and your child meet our scoliosis treatment team, you’ll discover we're always moving forward. Our physicians stay active in the medical community, continue their training and eagerly incorporate the latest evidence-based treatments for scoliosis into their practices. Often it is our own physicians developing the methods for these treatments, while working in partnership with the FDA and industry partners.
Every neuromuscular scoliosis treatment plan is as unique as your child. Read about all the scoliosis treatment options here and several of the most common below.
Observation
Sometimes the best treatment is time. Your child’s doctor will talk to you about the measurement of the curve in their spine and what that measurement means for his or her treatment. If the curve measures less than 20 degrees, our spine team will examine your child and take low-dose X-rays every four to six months during their growing years to see how the curve is changing (also called curve progression). In most cases, if the curve is not progressing, your child will not need treatment.
Scoliosis-specific Exercises
If your child does not wear a back brace, they may safely perform scoliosis-specific exercises. They'll be shown how do to them by our trained and certified therapists, learning individualized exercises to improve the alignment of their posture and minimize the progression of the spinal curvature. They'll perform these exercises daily to increase their strength and maintain the correction. This approach addresses the 3-D characteristics of scoliosis and is based on the Schroth method.
Mehta Casting
Mehta casting is an option for children typically between 6 months and 5 years, and it can be used instead of bracing. Casting is often used to delay or prevent the need for surgery.
A Mehta cast is a plaster cast applied from a child’s collarbone to the bottom of their spine. Once the cast hardens, it holds the spine in position by applying gentle pressure. Children need a new cast every two to three months, with each one straightening the spine a bit more. Some children may transition to a brace as they get older.
Bracing
Our orthopedic physicians may recommend bracing if the curve is moderate (between 25 and 40 degrees) or if it is progressing. The brace will need to be worn until your child stops growing, or until their doctors recommend a different type of treatment. It's important to note that bracing is not always effective and sometimes the curve increases anyway. In this instance, surgery may be necessary.
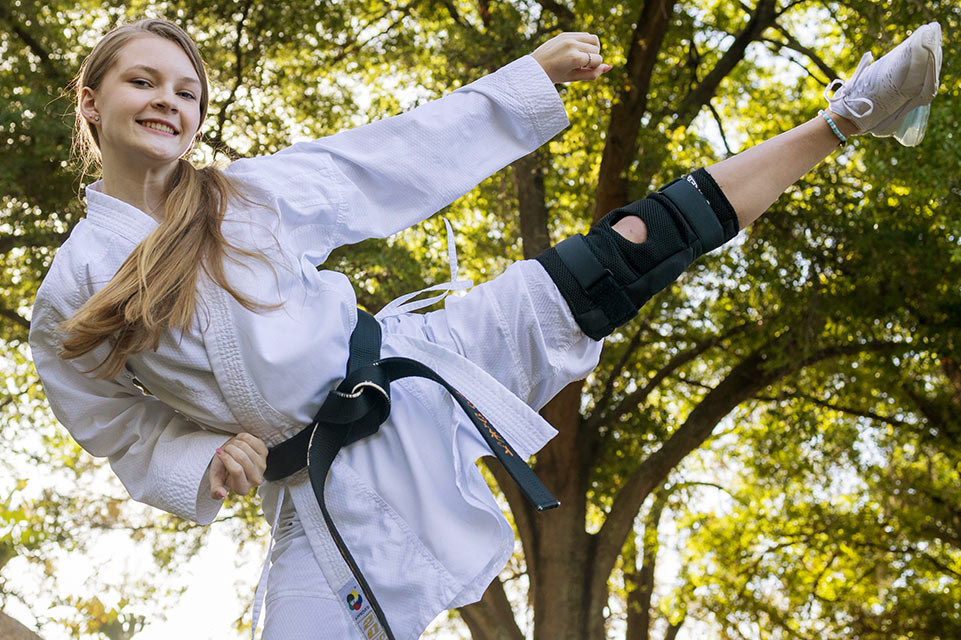
Halo Traction
This is a unique form of treatment for severe cases of scoliosis, offered at a limited number of pediatric hospitals in the United States. Shriners Children’s is finding excellent results with halo traction, an in-patient treatment option.
The halo is a ring device held in place on a child’s skull using several pins. It is held upright through a pulley system attached to a bed, a wheelchair or walker. A child’s head is lifted upward to lengthen the spine and stretch out surrounding soft tissue. By stretching the spine, there is an increase in the vertical height of a child's chest, which improves lung capacity and breathing.
On average, patients see a correction of 35% or more after three to four weeks in traction. A halo treatment is followed by spinal correction surgery to maintain this significant improvement. A team of child life specialists, physical/occupational therapists and other members of the care team partner with our surgeons during a child’s long-term stay at Shriners Children's for the halo process. The result is often life-changing.
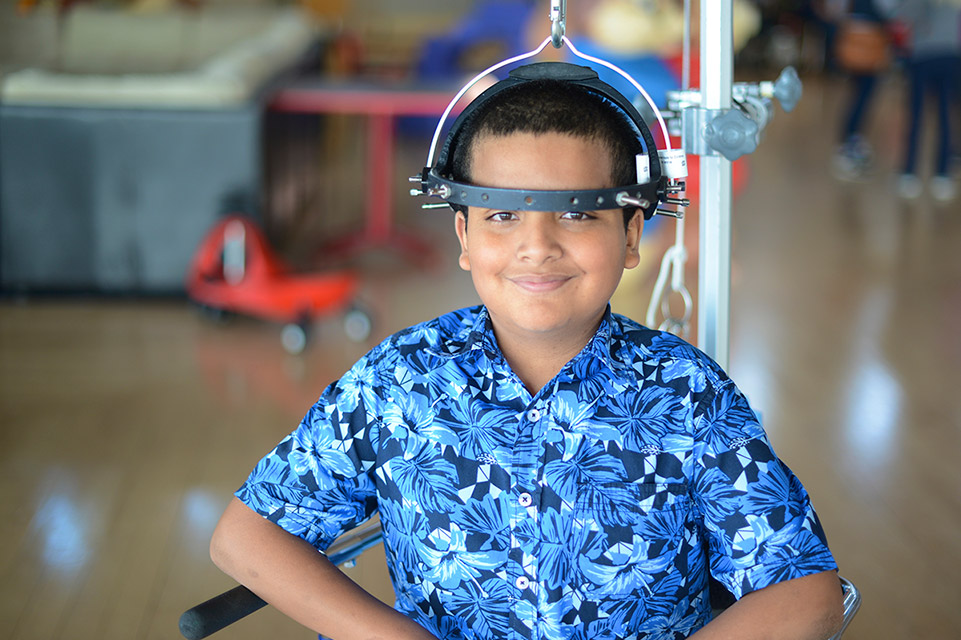
Growing Rods
During a surgery, two telescoping rods are inserted through the back and attached to the spine above and below the curve, with hooks or screws. Children return for treatment every six months to have the rods lengthened to match their growth. With a growing rods treatment, the spine continues to grow while being guided by the rods to create better alignment of the spine.
MAGEC Rods
The MAGEC (MAGnetic Expansion Control) spinal bracing and distraction system is composed of two magnetic, telescoping rods that are gradually lengthened from outside of the skin using a magnet. This pioneering procedure for young children with scoliosis helps reduce the number of surgeries they may experience during childhood, which decreases their exposure to general anesthesia and limits the number of incisions they would experience over several years.
Vertebral Body Tethering
Our pediatric spine surgeons are leading the way in this treatment. The Vertebral Body Tethering System differs from a typical scoliosis surgery called a “spinal fusion,” which involves implanting stiff metal rods along either side of a child’s spine to straighten the curve.
Rather than stiff metal rods, The Tether™ uses a strong, flexible cord attached to the spine. When the vertebrae are pulled by the cord, it puts pressure on the tall side of the vertebrae on the outside of the curve. This pressure slows the growth on the tall side of the vertebrae, so that the short side can grow and catch up. The system permanently straightens the spine using a child’s own growth process. Unlike spinal fusion, the spine is still able to bend and flex, rather than being fixed in place with the stiff metal rods.
Spinal Fusion Surgery
The goal of this surgery is to fuse the spine, correcting the spine curvature and preventing further progression. Fusion surgery involves attaching rods, hooks, wires or screws to the curve and placing small pieces of bone over the spine. The bone pieces (taken from the child during surgery or donated) will grow together with the child's spinal bone, fusing it in the proper position. Although the spine may not be made completely straight, the curve will be less than it was before surgery.
A surgeon may recommended spinal fusion for a child who is at least 10 years old with a curve greater than 45 degrees and increasing; or for a child whose curve is greater than 50 degrees once they have finished growing.
Shriners Children's care for Skylar's neuromuscular scoliosis has made all the difference for better breathing and skills to make him more independent.

Mehta casting works with developing bones to correct spinal curve
Innovative Treatments
View All Related Treatments
Mehta Casting

Bracing

Halo Traction

Growing Rods
MAGEC System

Spinal Fusion Surgery