Electrical Burn Care
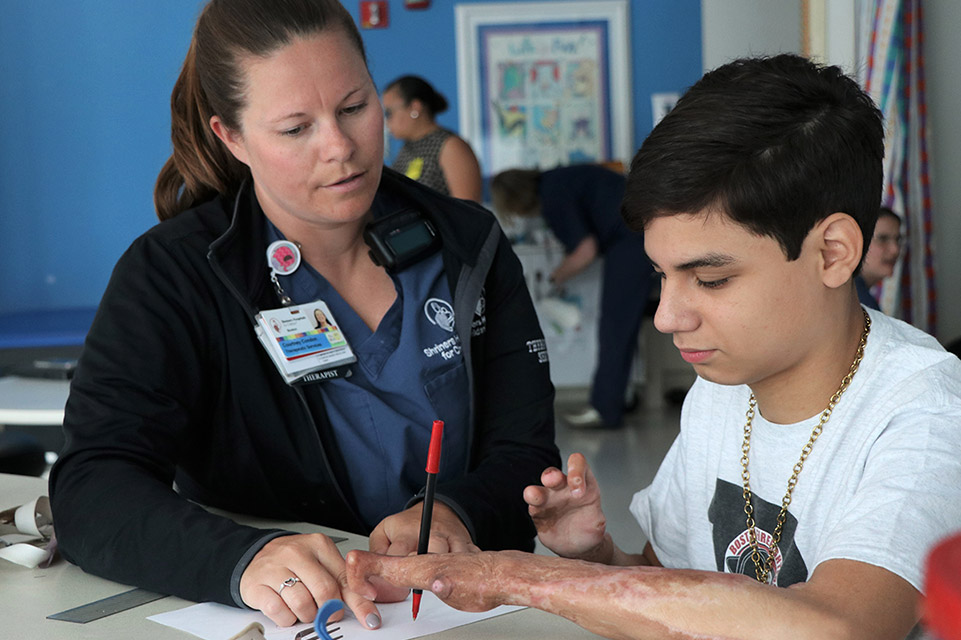
For over 50 years, our team of burn care specialists at Shriners Children’s has been taking care of children with complex and serious burn injuries.
What is an electrical burn?
Electrical burns are caused by exposure to household or high voltage electrical current. We have all heard stories of children receiving serious injuries caused by electrical burns. A toddler places a finger into an electrical outlet, a school-age child touches a high-tension wire on a dare or a teenager is struck by lightning in an open field.
Electrical burns can be devastating. Small surface wounds on the skin may be associated with larger internal injuries. Be reassured that if your child suffers an electrical burn, the care team at Shriners Children's is prepared to care for your child immediately following the injury and over time. The treatment of burn injuries is unique. Serious burns require precise, personalized care over the span of many years.
At Shriners Children’s, all of the specialists your child may need will be available when you come for care. Your child’s surgeons, nurses, physical and occupational therapists, and care managers understand the concerns of children and parents navigating this journey. With the most innovative treatments available, your child will be cared for by leaders in the burn care medical field throughout the duration of their recovery and childhood.
Shriners Children's Burn Care Accreditation
Three Shriners Children's locations providing burn care are accredited by the American Burn Association (ABA) and the American College of Surgeons (ACS) as verified pediatric burn centers.
We have a strong connection to and history with the ABA. All of the Shriners Children's burn care chiefs of staff at the above locations have been presidents of the ABA. These distinctions display the depth of the burn care support services we provide, as well as the vast amounts of research we lead on behalf of our patients and children around the world who’ve been burned.
Specific treatments and services may vary by location. Please contact a specific location for more information.
Emergency Treatment of Electrical Burns
Burn injuries are painful and frightening. In the moments after a burn happens it is most important to stop the burning process. Many people do not realize that burns can continue to worsen even after the initial contact.
- When an electrical shock injury happens, it is critical that you do not touch the injured person if he or she still is in contact with the current source (you may also become injured).
- Turn off current.
- Seek immediate medical attention and call 911 if necessary. Once the injury has been assessed in an emergency setting, seek care at a healthcare facility with pediatric burn expertise.
A Reference for School Nurses on First Aid Burn Care for School-Age Children
Burn injuries are among the most painful injuries any child can endure. School nurses are at the front line when children are burned at school. An 8-year-old boy comes to your office with redness and blistering on his right forearm after he accidentally spilled hot soup on himself. A 14-year-old girl splashes chemicals on to her hand during science class. These children are in pain and in need of immediate treatment. What should you do?
This guide covers types of burns, initial assessment and first aid treatment, and how to determine when a child needs to be evaluated by a physician.
What is a burn?
A burn is an injury to the skin from an energy source, including heat, chemical, electric or kinetic. Scalds or burns caused by hot liquids, are the most common cause of burn injury in young school-age children. At 150oF, it takes less than one second for a deep burn injury to occur. At 120oF, it takes two minutes of contact.
How do I assess the burn?
When assessing the burn, note the depth, size, and location of the injury.
What are the degrees of a burn?
The depth of a burn depends on how many layers of skin the burn penetrates. It is important to keep in mind that a burn will continue to progress in depth for the first 48-72 hours, so follow-up assessment of the injury is mandatory to accurately determine depth.
- A first-degree burn can be considered a superficial burn as it affects only the epidermis. The skin remains intact but is reddened. These burns are painful initially. Fortunately, the redness and the pain will subside in three to five days and no scarring usually occurs.
- A second-degree burn has gone through the epidermis and affects the dermis, which is the deeper layer of skin. Blistering occurs because of the skin damage. The exposed dermis is pink and can vary from moist to dry depending on the depth of the injury.
- Superficial second-degree burn wounds can take from 7-21 days to form the first layer of fragile new skin. This new skin can then take another one to two months to mature back to usual thickness. The color will often take several months and sometimes up to a year to return to the usual pigmentation. Usually, superficial second-degree burns do not form raised scars.
- Deep second-degree burn wounds can take four to six weeks before the wound can finally close. These wounds are at increased risk of forming raised scars.
- A third-degree burn goes through all the layers of the skin down to the subcutaneous tissue or even deeper. These burns can be deceptively painless because the skin nerves have been destroyed. A third-degree burn will appear leathery and have no noticeable blanching. These wounds require surgical skin grafting for treatment.
How do I assess the size of the burn?
For small burns (smaller than a handprint), a ruler can be used to measure in centimeters. For burns larger than a handprint, you can obtain a quick estimate by using the child’s hand. The area of the hand (palm + fingers) is approximately equal to 1% of the total body surface area (TBSA). Burn specialists prefer to describe burns with regards to percentage of TBSA.
In general, burn injuries larger than 5 cm (or 2 inches) in diameter should be seen as soon as possible by a medical provider.
When does a student need to be sent directly to the emergency room?
The American Burn Association suggests the following criteria for urgent evaluation of a burn injury:
- Second-degree burn injury greater than 10% TBSA (which is approximately an entire arm from hand to shoulder)
- Any third-degree burn injury
- Burn injuries to sensitive areas (eyes, face, joints, genital region)
- Patients with medical co-morbidities
- Any suspicion of child abuse
How should I initially manage a burn?
The first steps are to stop the burning process! If emergency assistance is required, call 911.
- For all thermal burns, remove any affected clothing and cool the area with cool running water for at least two minutes. Avoid applying ice packs – ice will cause vasoconstriction, decreasing the blood flow to the wound, potentially worsening the injury.
- Chemical burns require ample irrigation with water to remove wet chemicals from the skin. Dry chemicals should be brushed off first, before starting irrigation. Eyes injured by the chemical agent should be flushed with either water or saline for at least 20 minutes and then sent for evaluation by a medical provider.
What should I do about any blisters?
For patients going to see a medical provider, the blisters may be left intact. Pain from a burn wound can increase significantly once the wound bed is open to air. Pain medication is recommended prior to unroofing of blisters.
How should I cover the burned areas after cooling and/or irrigation?
If the patient is being sent to a medical provider immediately, just cover the burn wound with a clean, dry dressing.
Otherwise, if the student is going home after school, to provide comfort and decrease risk of infection, a dressing of bacitracin ointment with gauze bandage should be applied to the burned area. Bacitracin ointment will cover the most common bacteria on the skin. Triple antibiotic ointment can also be used if bacitracin is not available.
Who can I contact if I have any questions or am uncertain about the burn injury?
If emergency assistance is required, call 911. Your closest burn center will always welcome inquiries and questions. Shriners Children’s operates verified burn centers in Massachusetts, Ohio, Texas and California.
From the bottom of my heart, I’m so grateful for everyone at Shriners. They returned my life back to me.

Occupational Therapy Following Burn Injury
Innovative Treatments
View All Related Treatments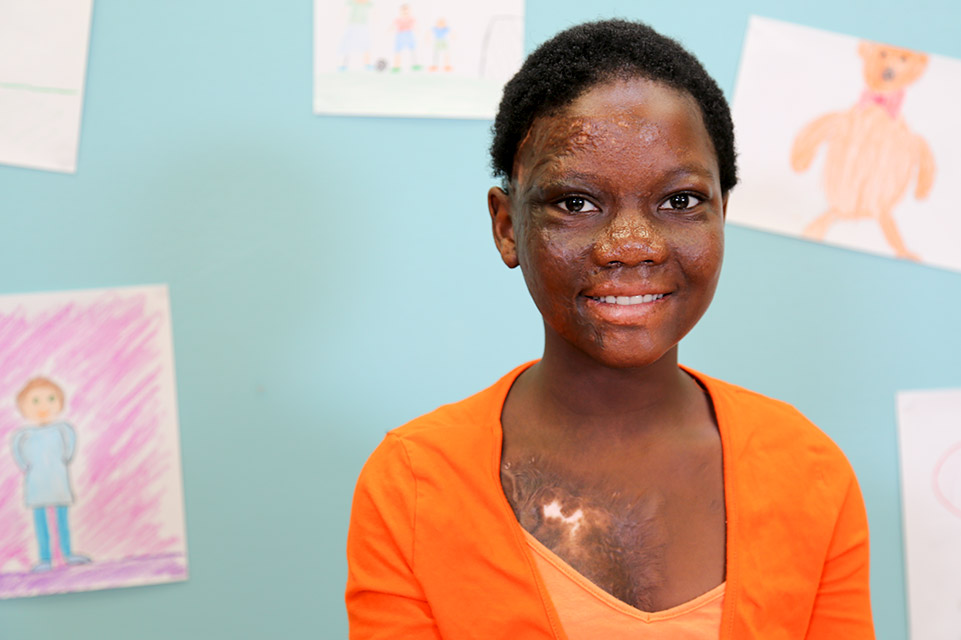
Plastic Surgery

Reconstructive Surgery

Inpatient Rehabilitation Following Burn Injury